Trending
Opinion: How will Project 2025 impact game developers?
The Heritage Foundation's manifesto for the possible next administration could do great harm to many, including large portions of the game development community.

Featured Blog | This community-written post highlights the best of what the game industry has to offer. Read more like it on the Game Developer Blogs or learn how to Submit Your Own Blog Post
While 168 million global subscriptions present a significant opportunity for broader reach and steady revenue, developers are treading carefully.

Game subscription services, such as Xbox Game Pass, Apple Arcade, and PlayStation Plus, have introduced a new paradigm in the industry, promising benefits to both players and developers. While the 168 million global subscriptions present a significant opportunity for broader reach and steady revenue, developers are treading carefully.
A July 2024 survey of the Game Developer Collective reveals that while many developers are optimistic about including their games in subscription services, few are tailoring the design of their games specifically for these platforms. No doubt, the slowing uptake of game subscription services post-pandemic has been a key factor in this restrained approach.
This is in contrast with the experience of other industries, such as music, where streaming services have had a significant impact on songwriting, with artists adapting to fit algorithms and playlists. The key difference is that music subscriptions account for over two-thirds of industry revenue, compared to less than 10% for games – meanwhile, game developers face a far more opaque payout model.
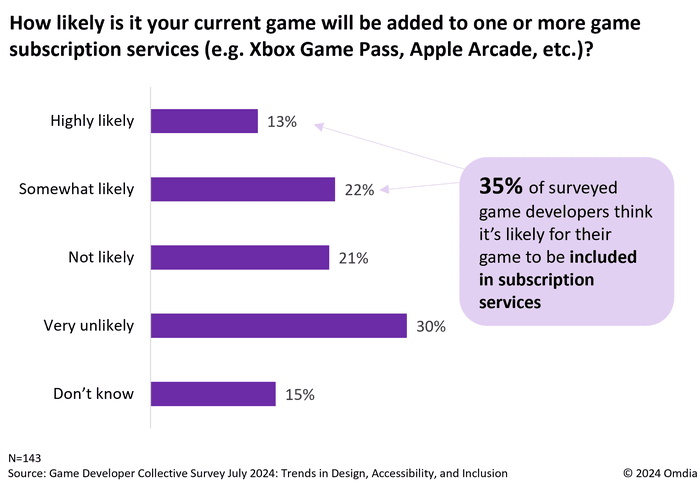
According to the survey, 35% of game developers believe it’s likely that their current game will be added to one or more subscription services. However, when asked if subscription models have influenced the design of their current game, only 13% indicated that subscription services have had any impact on their development process. A striking 80% said these services had no influence at all. These numbers reveal a gap between interest in inclusion and active adaptation to the unique requirements of subscription platforms.
Limited design adaptation points to industry hesitation about subscriptions
Uncertainty about how subscription services will impact developers’ revenue models long-term is likely at the core of this cautiousness. The most successful subscription platforms, like Xbox Game Pass, often provide developers with lucrative upfront payments in exchange for including their games in the service. But for smaller titles or those without obvious blockbuster potential, the ambiguity around whether their games will be selected for a subscription service makes it hard to rely on subscriptions as a revenue stream.
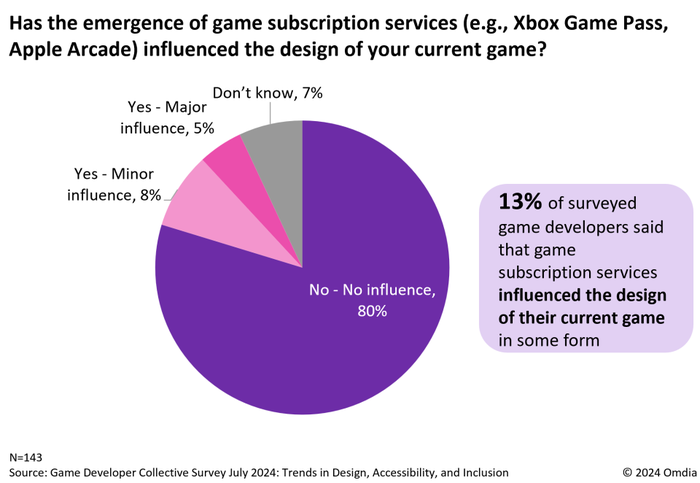
Games designed with subscription models in mind need to hook players quickly, as subscribers have access to a large library and can easily move on if they aren’t engaged early. A separate consumer survey conducted by Omdia found that four in ten subscribers try new games for only 30 minutes or fewer before deciding to commit. Yet, 80% of surveyed developers were reluctant to make substantial design changes, like front-loading exciting content right at the start of the game, that might favor these platforms (see chart above).
Opportunities offered by subscriptions remain alluring to developers
Despite the reluctance to change game design, the overall appeal of subscription services cannot be denied; 35% of developers expect their current game to be added to a subscription service (see the chart below below). Developers recognize the potential to reach a broader audience, particularly through services like Xbox Game Pass, which boasts over 34 million of subscribers worldwide. For some developers, inclusion in these services provides exposure to players who may not have encountered their games otherwise. The lure of increased discoverability and the potential for long-tail revenue has led some studios to start exploring these platforms, even if they aren't overhauling their design strategies just yet.
However, these benefits are tempered by the slow subscriber growth all platforms are experiencing. After the pandemic-induced surge in 2020 and 2021, subscriber growth has slowed significantly, and while steady growth is still expected in the years ahead, the massive consumer adoption some industry players envisioned remains distant. While subscriptions will generate $19.4bn in 2024, this will still make up just 8.8% of global games content revenue this year, according to Omdia’s latest report on the game subscriptions market. But while subscriptions will not dominate the games market, they will complement a diverse range of monetization approaches. Therefore, the path forward will likely involve cautious experimentation – balancing the allure of subscription platforms with the economic realities of game development.
You May Also Like