Trending
Opinion: How will Project 2025 impact game developers?
The Heritage Foundation's manifesto for the possible next administration could do great harm to many, including large portions of the game development community.

Featured Blog | This community-written post highlights the best of what the game industry has to offer. Read more like it on the Game Developer Blogs or learn how to Submit Your Own Blog Post
Changing driving seat for game development is an important decision and it requires through understanding of game life cycle. Know at what stage your product is and which mind set should be at driving seat.

Mobile Game life cycle can be explained in four stages based upon the physical presence of product. In first stage a new product will be "In Mind" of a game designer, developer or investor. In second stage it will come "On Papers" in front of a game designer. In third stage it will start taking shapes "In Computers" at desks of creative designer, artists, developers and game-play testers. Finally it will be "In Markets" at different stores and in the smartphones of customers.
Although being in the right mindset for your product at right stage is important but you always need a leader to make sure all ships all sailing in the right direction.
Following Image summaries the major activities performed at each stage.
.png/?width=600&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
Stage 1: In Mind
Having a game idea is the first step and it does not matter whether you are going for cloning, re-skinning, improving or innovating an idea. Important thing is the feasibility of your idea. Do extensive home work for idea selection and idea refinement.
In order to draft Idea feasibility make sure you get enough understanding of your customers, competition and company.
Customer: Personify your target customers and more importantly know their psychographics to know their attitudes, colors preferences and values your idea is going to offer.
Competition: Identify your actual or potential competitors and know their strengths and weaknesses. This will help you in adding competitive advantage in your product and later will guide your marketing strategies to hunt well in red oceans or blue oceans.
Company: One should never skip this analysis to make sure all the relevant knowledge and expertise are present throughout the life cycle implementation.
Marketing mindset dominates this stage but a game design mindset should be present to assist. Surprisingly many people have developed both mindsets and they are earning well :)
Stage 2: On Papers
Once your idea passed feasibility test and show market potential along with guidelines to penetrate in the market you start paper work. There are four major areas to focus at this stage.
Game Mechanics: This is the heart of your game and offers value to the end user. Think about user interactions, controls and execution of the game play to offer maximum entertainment to the customer. In other words game designer has to draft the main game play, core play loop and game HUD.
Game Flow: Draft the wire-framing for your product. Design all supported screens, dialogues and pop-ups. Every tap or click made by user has significant importance so either it should offer value to user or to the business. Avoid extra screens and complex navigations because I have never observed 100% conversions at any tap.
Game Progress: Think about displaying user progress; "No one plays a game to lose". This factor counter most in game retention and money comes with high retention. Level designs, scores, unlocking contents and many more techniques come to play simultaneously.
Game Economy: Design your hard and soft currencies and control their sources and sinks to create pressure points and roller coaster experience for the user.
Along with above mentioned four areas one should also take into consideration the following two minor facilities as well.
Extended game loops: Core game play loop is the heart of game play but still one can add more entertainment with extended game play loops. The more these loops tighten to the core loop the more value it will offer. Mini games also offer some extension to the game play loops so consider them as well.
Monetization Gamification: Earning money from a game play isn't a direct output. In game design phase implement gamification for monetization. It can be by-passing time gates, selling of props, opening of hard gates or making progress over-night with real money. On the other hand majority players prefer to play for free so there should be ads mechanism, rewarded videos or cross promotion options to monetize free players as well.
Stage 3: In Computers
Normally stage three activities starts in parallel to stage two for multiple iterations and refinement of basic game design decisions already taken. Following major activities are performed at this stage and I am not going to discuss them in detail.
Concept creative
Creative Art Work
Game software development
Design and implementation of analytics frameworks
Integration of free monetization tools (Ads networks)
Design and execute game simulation to cross check game progress and economy design.
Company analysis done at stage 1 is critical for these activities to avoid road blocks and hurdles down the road when costs have already incurred.
Stage 4: In Markets
This is the most important and longest phase in game life cycle. In this phase key to success lies in being data centric. In start one should focus on monitoring and improving the traditional game funnel explained in below image (Do not use funnel approach for marketing activities)
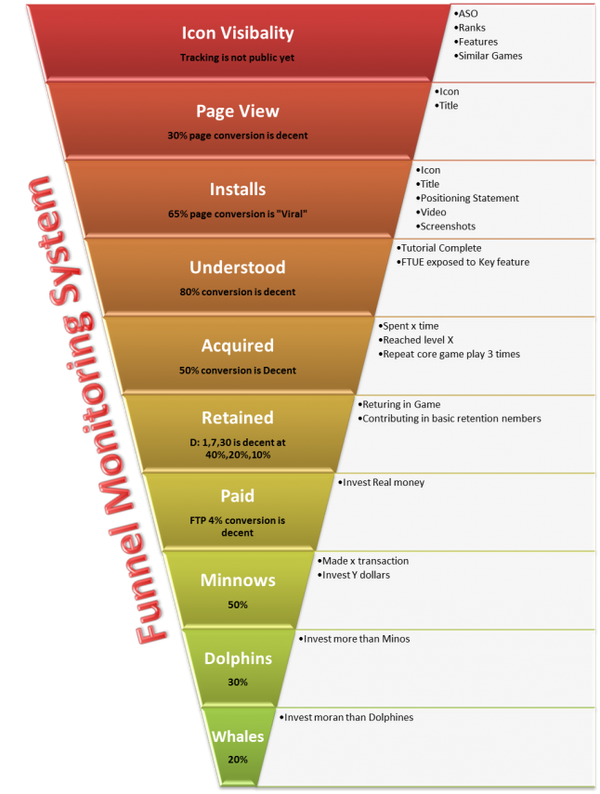
In parallel to monitoring and improving game funnel many marketing and selling fronts open and special support and execution teams come to life. Following are some of the key areas to be focused at this stage.
Organic Growth: Get control of all the organic growth levers and keep them updating on regular basis. ASO is the most successful tool, yet presence on web, in similar apps, in ranks, in feature games also contributes a lot to growth.
K-factor Play: K-factor also known as social-factor; plays important role in being viral. In order to be viral one has to cross the chasm and integration of social features in games and social marketing techniques becomes the useful tools. Social features can also be integrated to achieve high retention, to enhance sense of achievement and to increase the presence on web.
User Acquisitions: User acquisitions techniques operate under the guidance of business objectives. Business objectives can be to bring a decent look of game page, to establish a prominent position, to compete, to add barrier for new entrants or to earn money. Monitor and measure all of your user acquisition channels for better decision making and achieving business goals a.s.a.p.
Customer Support: A customer who contact you worth 10,000 users; if you have closely looked at the game funnel. So every time take them seriously and always be on your toes to support and facilitate them.
Live-Ops: Game development and design does not end at stage 3. There is still a complete module to execute on regular basis. Live Operations deals with ongoing activities in the game and can take many forms like tournaments, seasonal activities, regular competitions, time bound activities and periodic sales. Live-ops team also have to be in touch with the activities happening around the end users like valentine days celebrations or some major sports event occurring.
Game development is a multi-billion and rapidly growing industry and basis on which it is playing; can't be covered in one article. Still I try my best to cover the major roles and activities constructing the foundation of the industry.
Read more about:
Featured BlogsYou May Also Like