Trending
Opinion: How will Project 2025 impact game developers?
The Heritage Foundation's manifesto for the possible next administration could do great harm to many, including large portions of the game development community.

Featured Blog | This community-written post highlights the best of what the game industry has to offer. Read more like it on the Game Developer Blogs or learn how to Submit Your Own Blog Post
A postmortem about Heartonomy's iOS game StarLicker. The game was not a success, and in this article the developers reflect on the mistakes that were made and what they learned from them.

This article originally appeared on the Heartonomy company blog at http://heartonomy.com/2014/04/reflections-on-an-indie-failure-starlicker-postmortem/
Development on StarLicker began in April 2012, and it was Heartonomy’s first game project as a company. We released it in August 2013 and continued working on it for several months after the release. A total of 5 people worked on the project, and while I (Hayden) had worked with everyone previously, this was the first time that everyone else had worked together.
StarLicker was an unsuccessful game in almost every way imaginable. We made a lot of mistakes on this project, but through this process, our skill, knowledge, and wisdom as game developers improved dramatically. This article is meant to record our experiences so that we improve going forward and to share what we learned with others who walk in similar shoes. In this business, we hear a lot about the success stories, but not as much about the failures. So here we go…
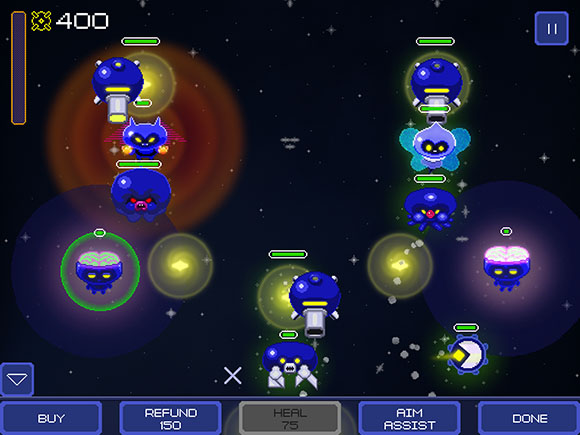
Hayden: I began the SkySwitch project, as it was originally named, wanting to build the game around high level design goals. The first goal was to build a strategy game with the aesthetic of a bullet hell shmup. Early into prototyping, the concept of the opposing players “feeding” each others’ economies through aggression emerged, and I fell in love with that as a design goal as well.
To this day, I still think at a high level StarLicker represents an interesting, original game concept with a lot of potential. This is one of the few areas where the released game is very strong, and a lot of feedback we’ve had from players confirms this. However, this was also the first strategy game I designed and the actual game fails to capture the full potential of the concept.
Rudd: Some time after Hayden started Heartonomy and StarLicker but before I joined the project, we were participating in a small hackathon together, and I got a chance to see the prototype. At that point, even though it was extremely rough looking, I could tell that the main mechanic had a lot of promise, and I was seriously impressed. With my naive attitude towards the game industry, I believed that a concept this original and innovative was sure to do well if it could be executed on. The concept is what really sold me on joining the company and risking my livelihood. While there are a ton of things I’d do differently now, I agree with Hayden: I believe that the concept was one of the better aspects of the project.
Hayden: Personally, I find it a bit trifling to celebrate the mere release of a game. Having said that, I recognize that shipping does represent a real accomplishment. It requires crossing the t’s and dotting the i’s and there is a lot to learn just from this process alone. If we had not released anything, then writing this article would hardly even make sense.
Additionally, it was always a secondary goal of the project from the very beginning to create a game that could serve as a portfolio piece to showcase to potential work-for-hire clients. We had no illusions that our first release would magically become a huge hit game that could fund the company for the rest of time. We knew it was likely that we’d have to resort to contract work at some point to stay afloat, and that is exactly what happened. And StarLicker has already successfully demonstrated to clients on more than one occasion that we know how to build and release a game.
Rudd: I disagree with Hayden that shipping is “trifling”. To me, shipping the game was a major accomplishment. The difference between an indie studio that has released no games and an indie studio that has released one game is infinitely large. I’m extremely happy that things like Game A Week are becoming popular, because that mentality would have helped immensely at the start of this project. The months leading up to the first release of StarLicker were extremely stressful for me because I could feel that something was wrong. Even with so many months of work put into the game, I could tell that we hadn’t really done anything. We needed to ship. When we finally did, even though the reception was poor, I felt much better, like a weight had been lifted off my shoulders.
Hayden: I had heard this phrase countless times before but I never truly understood it until recently. In fact, I had heard all of these lessons before, but alas, I am the type of person that learns best by doing (it wrong). At the outset of the project, I had just quit my job and started My Own Company and I was higher on naive optimism than I’d ever been before. For game design, I thought it was enough to establish specific, clear high level design goals (described above) and the rest of the design process would follow naturally and easily from that. This was extremely incorrect.
Nothing about the process of game creation is particularly natural or easy. Every bit of it requires special skills and talents and tons of practice, and design is no exception. I could probably write an entire book about everything I learned about game design from this project, but we’ll keep this to the big ones.
Hayden: Playtest early and often. The value of fresh eyes on a game can not be overstated. It’s fine to start with coworkers, friends, and family, but they will grow accustomed to the game quickly and thus cease to be effective playtesters. As soon as the smallest nugget of the game is playable, start having people play it, and then never stop finding new people to play it at every step of the way.
Hayden: Really, actually listen to playtest feedback. Playtesters say lots of different things after they try a game. The designer will disagree with all or even most of their suggestions. But do not dismiss any feedback, as I did, with the attitude of “this game is not for you”. It is the responsibility of the game designer to listen to and analyze every single bit of the feedback, and discover precisely what truths it contains. Often, this truth will be far from obvious and often not even directly related to the actual feedback itself. But everything a playtester says, whether its something they like or don’t like, or a new idea they have, comes directly from their experience playing the game, which means there’s something to learn about the game from it.
Rudd: To me, this is the most tragic failure of StarLicker. When we submitted to IndieCade for 2013’s festival, they were nice enough to provide feedback to all entrants. This feedback should have been invaluable, coming from people who understand indie games and what makes them worth playing. But with this feedback, we almost entirely rejected it out of hand, believing we knew what was best for the game.
If I try to rationalize why we thought it was reasonable to ignore, it might be that one of the judges said that they’d love to be able to try the game via multi-device asynchronous play, which was already in the game and in fact the main intended way to play. How deeply can they be looking at this, we thought, if they didn’t even see that? But other feedback cut to the core of what we now know to actually be the issues with the game. “You nailed everything but the core gameplay elements”, wrote one judge, with words that still sting to read.
Perhaps if we had listened better to feedback, we might not have such shocking stats on retention: only 6.8% of matches end quote-unquote “normally”, and almost 65% end in an automatic forfeit due to one player failing to play their turn.
Hayden: While I agree with Rudd about the value of the feedback we got from the IndieCade judges, I remember things differently about why we didn’t take it to heart. It actually began with a playtest session organized by the NYU Game Center specifically for IndieCade submissions. We came out of that playtest with lots of great feedback and some crazy ideas that would have been major changes to the game design.
However, this playtest took place in June 2013, which was already after when we originally wanted to release the game. I’ll get into this in more detail below, but at this point we were panicking over money, and no one was feeling brave enough to make major design changes at that point. This is why such valuable feedback was ignored.
Hayden: Start as small as possible. A multiplayer strategy game, even a small one, tends to be a very complex game design. To put it bluntly, I was simply in over my head as a game designer. Despite having a lot of experience playing these types of games and the clear design goals mentioned above, I did not have the experience or skillset as a game designer to execute well on those goals in the time we had to develop it.
Rudd: What we shipped was a much larger and complex design than we should have taken on for a first game, unconditionally. But what we originally planned to build before release was significantly more work than we actually managed to do. We originally planned a single player story mode, leagues with Elo/MMR systems for multiplayer, player messaging, and even, perhaps after launch, an innovative system for players to mentor other players. But even by cutting all that, it was too late. The original design necessitated at least some of those things to keep players engaged, but we had run out of time to deliver on them.
Hayden: In business, time is money and money is time, and we didn’t have enough of either for StarLicker. I originally intended for it to be a 3 month project, but then I decided to make it multiplayer. And then I decided to add 5 variants of each of the 8 units, four unique power-up abilities, etc. In other words, we let the scope grow wildly beyond what we could actually deliver on at the quality bar we wanted. To make matters worse, we were living off of our savings, and it’s frightening to watch your bank account balance dwindle, and this fear clouds good judgement.
We crunched for months toward the end, but while that allowed us to release the game (mostly) as designed, it forced us to rush on many aspects of the production that should not have been rushed. For example, we never created an automated system for integrating art assets. Every time an asset was modified, I had to spend time manually putting it into the game. We never felt like it was okay to slow down and really spend the time on “unnecessary” things like automation. At first this seemed acceptable, but by the end of the project we had thousands of art assets (all the animations are frame-based sprites) and this manual process ended up wasting so much time in the long run. The same was true for a lot of coding tasks that would have resulted in a more polished game. In the middle of a rushed, panicked crunch, it’s basically impossible to slow down to really get the code right.
So, just like in the AAA industry, the best games tend to come from the companies that can afford to say the release is “when it’s ready”, and the bad games always show signs of sloppy, rushed work. Game production is game production, and there is no exception for indie games.
Rudd: The caveat from this lesson learned that I feel we should emphasize is that this comes second to having a correctly-sized scope for your team. Yes, releasing a product that we weren’t happy with was a mistake, but I still feel that we made the right decision in essentially cutting our losses. We had spent as much time as I was comfortable spending on the project, so we basically had to release it before it was ready, because we had failed to scope the project correctly for our resources.
Hayden: This is a big one - the decision to make StarLicker a free to play game. The reasoning behind this decision went something like this: the best way to maximize the number of people that play the game is to make it free. And it would be no problem to design a free to play system that people will like because, well, League of Legends does it! This might be the best example of the overzealous idealism that pervaded the project, a theme you may have already noticed. The problem is that we knew what LoL did to monetize but we didn’t have a good understanding of why it worked, and completely failed to communicate a compelling “why” in our design.
Rudd: One of the biggest problems here is that StarLicker was a niche game. It is not easy to learn or get into. For some games, that is okay. But StarLicker being free meant those that downloaded it had no incentive to give the game a further chance, unless they had a friend bugging them to play it. If they had paid an upfront cost, at least some of them would feel obligated to “get their money’s worth” out of it and learn how to play.
Even for the players who did invest themselves into the game – time-wise, that is – the incentives to pay were extremely low. For the first 6 months of the game being available, we did not offer any cosmetics for purchase; the only IAPs available were XP multipliers and items that were also unlockable via normal play. Some player reviews actually expressed guilt over not paying since they were enjoying the game so much, but not enough guilt to actually purchase anything.
Hayden: Not only was StarLicker a niche game but it also had some design flaws that resulted in a severe player retention problem. This is a death sentence to any free to play game, let alone one that limits the maximum amount of stuff for sale so as to not “abuse” the model. So in the end, we made an extremely small amount of money. With around 11K downloads, the game has earned less than $300 to date (no I didn’t forget a zero there).
Hayden: Since day one, I wanted Heartonomy to focus on developing multiplayer games. So very early in the project, I decided to tackle asynchronous multiplayer as the focus for StarLicker. I enjoyed playing several async games on my iPhone, so it seemed like an obvious good idea. But the problem is we focused on multiplayer features so much that we entirely neglected all the value contained in playing solo.
I eventually came to realize that the value of single player is that most people simply prefer to learn a new video game on their own at their own pace. For most people, trying to learn an entirely new and unfamiliar game in the context of a competitive 1 versus 1 matchup is difficult and stressful. Add on top of that the fact that asynchronous means there is a lot of waiting between turns, and the result is a game that is almost impossible for new players to really get into.
Another side effect of ignoring single player is that we ended up rushing the creation of a tutorial that was little more than an afterthought. I feel like we missed a huge opportunity to make a compelling single player mode for StarLicker that could have introduced people to the game’s unique mechanics at a reasonable pace such that they would enjoy that learning process. And then, hopefully, most players would have eventually decided they were ready for the added challenge of competing against other players.
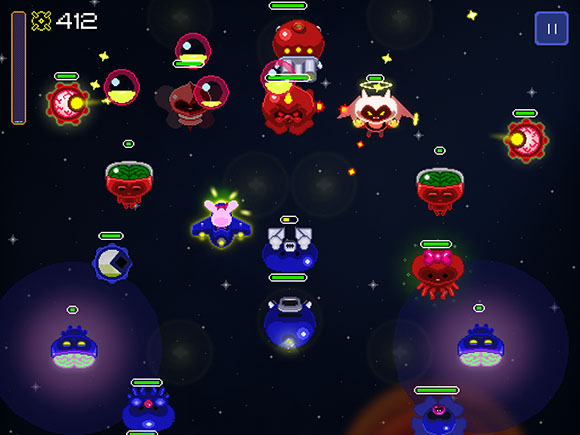
Hayden: Let’s talk for a moment about how we came to name the game “StarLicker”. I originally started calling it this as a new codename that I thought was hilarious and described the core mechanic of the game (tracing along the paths of star-shaped bullets) better than what we were calling it at the time – “Sky Switch”. As we asked more and more people what they thought of the name, we realized it was an extremely polarizing issue. Some people loved the name while others hated it. Those that loved it felt like it was unique, bold and intriguing. Those that hated it thought it sounded gross or perverted and said they would be embarrassed to tell it to other people. Ultimately, we decided to go with it, but I honestly still don’t know if that was the right decision. I’m still getting the same polarized reactions when I tell new people the name.
Rudd: Honestly, I never even liked the name. It always made me a little bit uncomfortable, like it was semi-NSFW. Of course, at the time of its naming, the main player character Lenny wasn’t flying around in a ship, but was flying on his own, with a giant tongue licking up the energy bullets. It wasn’t until later that I finally convinced the rest of the team that that concept was a little too out there. But the name stuck because of the polarized reactions. Our biggest piece of mainstream press coverage seemed like it came entirely from the audacity of the name, and the (NSFW) comments bear that out. At that point, it seemed like it could be one of our “angles” so the name was pretty much set in stone.
Hayden: Marketing an indie game is a ton of work and there is no clear formula to follow to find success. We knew how important marketing was, but we didn’t really know what to do about it. I feel like our marketing effort was halfhearted, and this was a direct result of the fact that we all knew, deep down, that we rushed the game out and it wasn’t good enough. The big advantage indies have when it comes to marketing is their unbridled passion, and by the time we finally released the game, we just didn’t have enough passion left in us to properly promote the game.
Rudd: The biggest marketing push for the game wasn’t even made by us. In fact at the time of this biggest push, I was packing up my apartment to move the next day, unaware that it was happening until it had already begun. Our friend Brian made a post on Reddit’s /r/gaming that made it to the top for a short period of time, even making it to the standard front page of Reddit. By Imgur’s estimation, Brian’s infographic was viewed over 413,000 times. That’s some serious exposure, for sure. By far that was our biggest spike in attention, accounting for almost 10K downloads, about 90% of all of our downloads ever. And we didn’t even have anything to do with it. Ouch.
Hayden: StarLicker was entirely self-funded by the development team. This meant basically no one got paid and the plan was that we would each get a slice of the profits after the game was released and the dough started rolling in. For the entire duration of the project, when it came to paying rent and bills and buying food, we each had to fend for ourselves. Rudd and I were full time on the project, so for us that meant living entirely off our savings. For William, it meant periodically taking time off from freelance gigs to focus on StarLicker art in focused bursts. Kurt was wise enough to force me to pay him a little something upfront, but it was a pitifully small amount and definitely less than what his contribution was worth. Zane, having just graduated from college, was an unpaid intern working for IOU.
But then we released the game and money did not start rolling in. It barely even trickled in. And this created a very strange and unexpected set of feelings beyond the obvious disappointment and frustration. I felt really strongly that I just completely let everyone on the team down. It was like I assembled a team of some of my most talented friends whom I had the utmost respect for, only to have them waste a huge chunk of their creative lives. This feeling still hasn’t worn off, and I don’t know if it ever will. This is a huge force fueling my desire to revisit the core concept of this game and the universe we created for it, so that maybe one day I can rest assured that it was all worth it.
Since long before I (Hayden) started Heartonomy, I’ve felt that making games was my purpose in life, that I had something important to contribute to the world through gaming. StarLicker was not the first time I’ve tried and failed to create a successful game, and it probably won’t be the last. But with each subsequent failure, it hurts a little less, and I learn a lot more. Eventually, hopefully, I’ll have learned enough to make and release a game well enough to succeed.
We set ourselves up to make a lot of the mistakes described above because we shut ourselves off from the world during development. The game dev community, especially indies, can help each other so much. I read once that we are not competing against one another, but we are all competing with obscurity. I believe this is true. So if you read this article and have any sort of reaction at all, we’d love to hear it. Whether it’s a question, something you can relate to, words of encouragement or even discouragement, please share it with us by email ([email protected]">[email protected]), twitter, etc. Thanks for reading.
Read more about:
Featured BlogsYou May Also Like